Computer Architecture, also referred to as “computer system design”, is a field of engineering and computer science that deals with the design of computer systems. It encompasses both hardware and software design elements, including the architectures of individual computers, computer networks, and large-scale systems. The goals of computer architecture include optimizing system performance, efficiency, and reliability, while minimizing cost and size.
Computer architecture involves the selection of hardware components, the design and layout of system components, the interconnections among components, and the definition of the instruction sets and other software programming specifications. It also involves the analysis of existing system designs in terms of their trade-offs, and the cost, performance, and reliability of the resulting design.
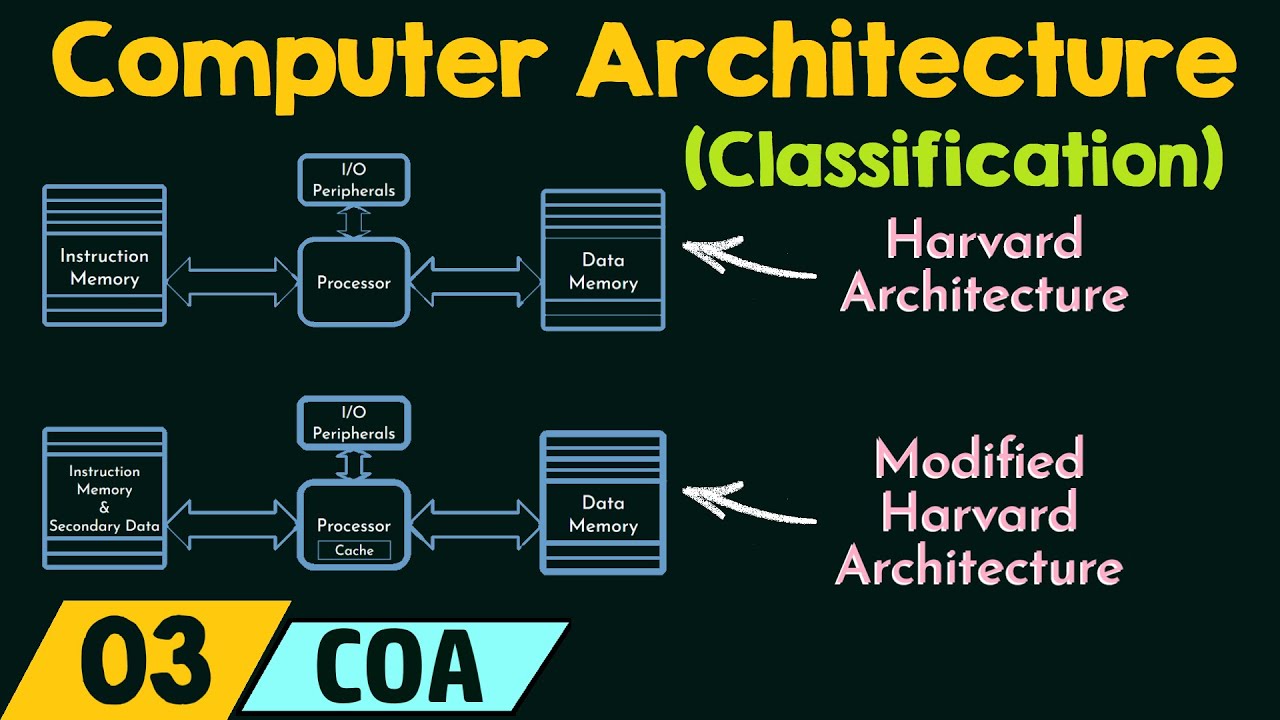
Computer architectures are divided into two components: the instruction set architecture (ISA) and the underlying microarchitecture. The ISA defines the computer’s instruction set, registers, addressing modes, and memory addressing. The microarchitecture, also known as the logic design, describes the machine’s organization and implementation.
Computer architecture has evolved significantly over the decades, and continues to do so. Recent advancements include nanotechnology-enabled hardware components, virtualization technologies, and the rise of cloud computing.
Computer architecture is used to design and build many types of computing devices, from the smallest microcontrollers to the largest supercomputers. It is important for student and professionals in the field of computer science to understand basic principles of computer architecture.