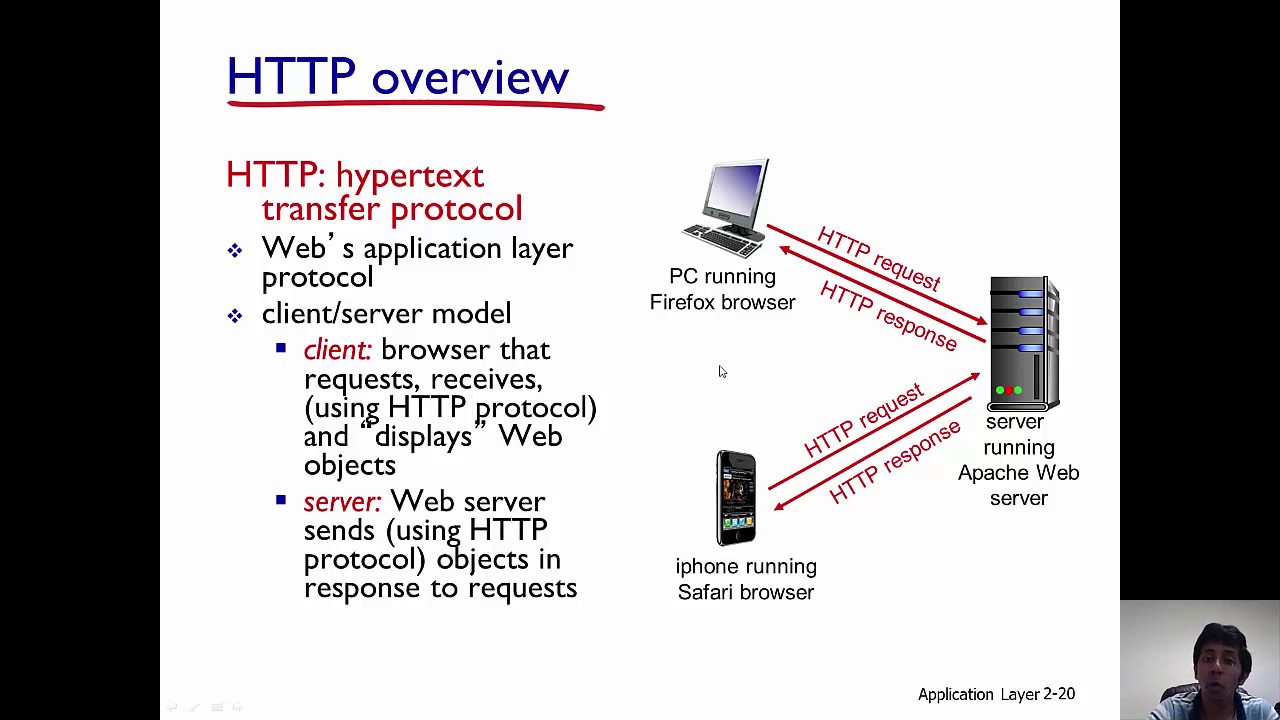
Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is a protocol used for exchanging information on the World Wide Web. It is part of the application layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite used by the Internet and is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web.
HTTP works by providing a way for clients connected to the Internet to send requests to servers, using the HTTP request methods. The methods defined are GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, HEAD, OPTIONS and TRACE. The servers, in turn, send the appropriate responses based on the requests.
The version of HTTP used today is Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 1.1. The earlier versions of the protocol are no longer in use. HTTP 1.1 is designed to make the web faster and more secure. It has several features that make it more efficient than earlier versions, such as persistent connections, pipelining, chunked encoding, and content negotiation.
The use of HTTP in websites has allowed for the increased functionality and interactivity of web applications. Many modern web services are powered by HTTP, such as blogs, websites, photo/video websites, streaming media, internet forums, and more. Browser-side languages such as HTML, JavaScript, and CSS make use of HTTP as a way to transfer data and render it in the browser.
HTTP is an incredibly important protocol in the modern digital world and is essential for the seamless functioning of the web.