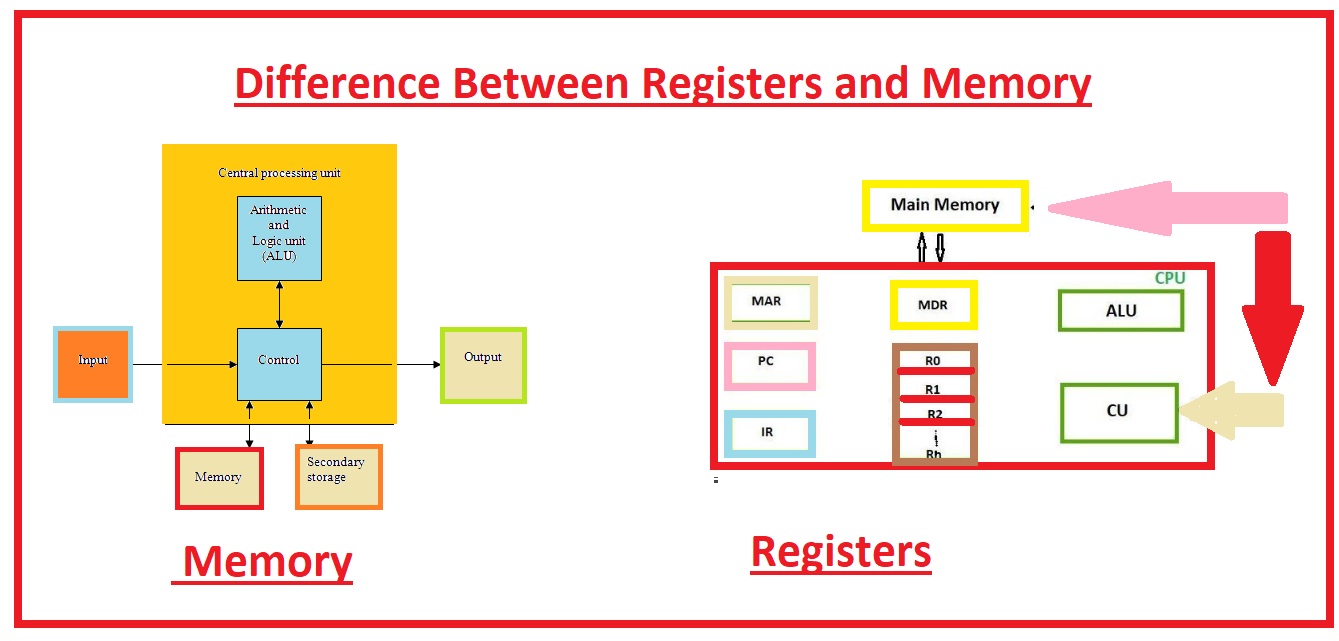
Memory Data Register (MDR) is a computer memory unit responsible for storing information temporarily as it is being processed through the CPU. It is one of the most important components of any digital computer system and is typically placed between the CPU and the main memory.
The MDR consists of a set of addressable memory locations, each of which can store a single byte or a word of binary data. It works in a similar fashion to a regular RAM or ROM device, but is considered part of the CPU rather than a separate component of a computer system. A MDR is composed of two parts: a storage register and a control register. The storage register holds the data bits and the control register is responsible for controlling the size of data being stored.
Data is transferred into the MDR from the main memory via an instruction called a “memory-fetch” and out of the MDR to the output device through an instruction known as a “memory-store”. Every instruction generated by the CPU will typically require the exchange of data between the MDR and the main memory.
The size of the MDR ultimately dictates the speed and performance of the processor as the frequency with which it can access instructions and data stored within it. A larger MDR enables the CPU to access information and instructions at a faster rate, while a smaller MDR results in slower operations.
Memory data registers are essential components of modern computer systems, allowing them to process data expediently.
References:
– “Memory Data Register.” Wikiwand.com.
– Choi, I. Sheldon. “Introduction to Computer Science.” Princeton University Press, 2021.