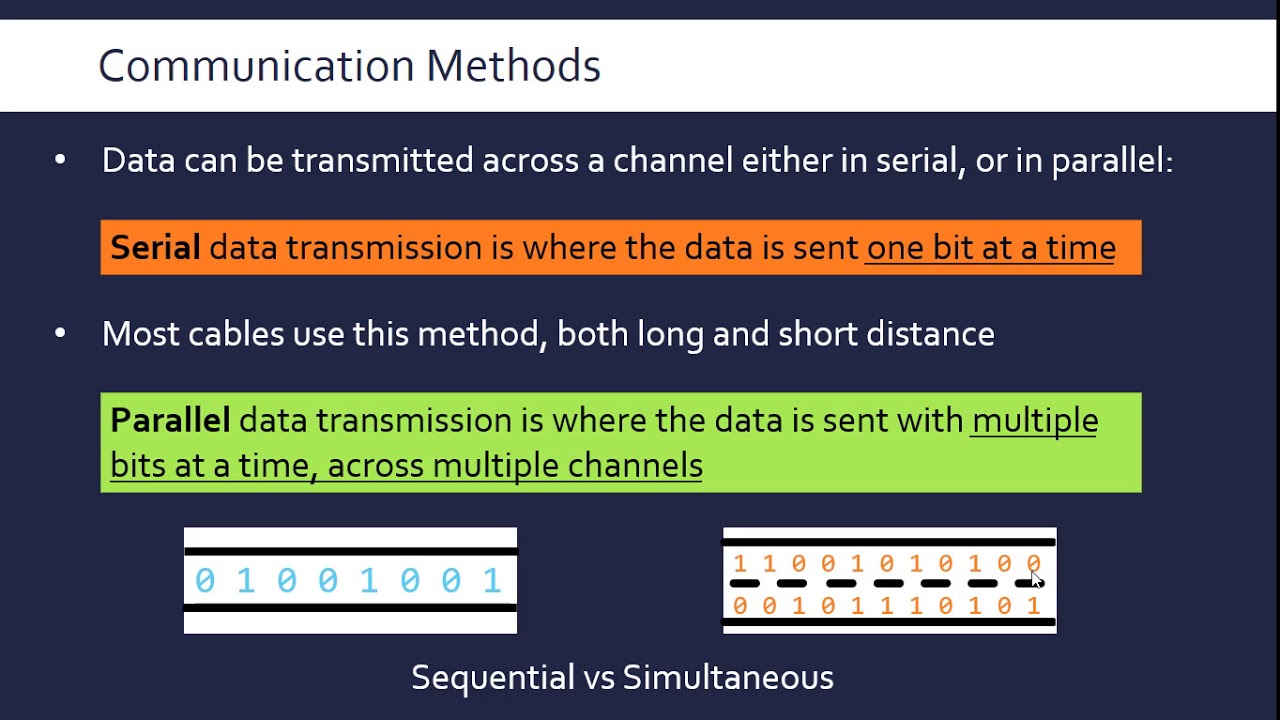
Parallel data transmission, also known as Parallel Transmission, is a type of device-to-device data communication whereby multiple bits of data are sent and received through multiple electrical or optical lines simultaneously. Compared with serial or asynchronous communication, parallel data transmission can send more information at a faster rate.
Serial transmission transfers data one bit at a time and usually requires only one data line. Parallel transmission involves the simultaneous transfer of one or more data words, where a data word is the unit of data processed as a set in parallel communication. This is achieved using a device-to-device connection with multiple cables that transmit and receive data simultaneously, resulting in a faster transfer speed due to the increased parallelism.
Parallel communication is typically used in applications where data rates or bandwidth needs are higher than that of serial communication, such as when you need to transfer large amounts of data over a short distance. It is commonly used in computer systems to connect devices like printers, scanners, and external hard drives to a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). Parallel data transmission is also used in the Local Area Network (LAN) to connect multiple computers within a network.
Due to the greater speed and higher bandwidth of parallel communication, it is typically more expensive to implement than serial communication. In terms of overall system performance, parallel communication is usually the preferred choice when speed is the most important factor.