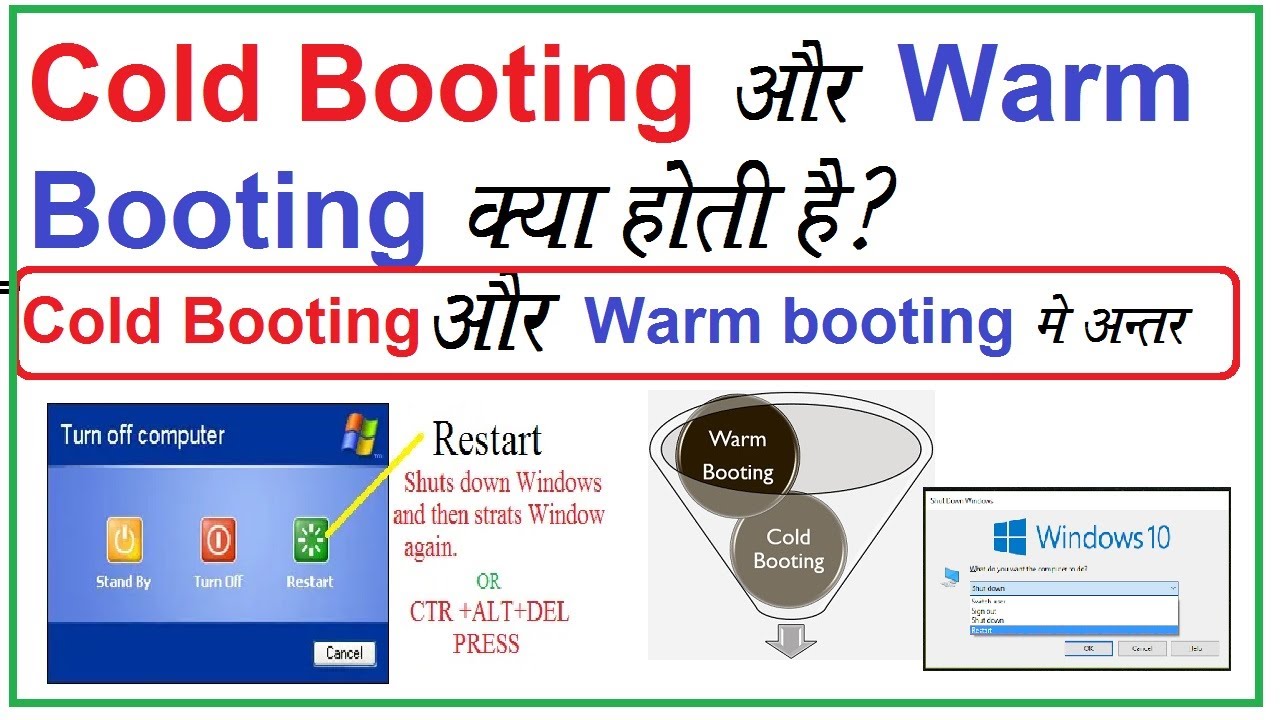
Warm Boot is a computer restarting process that launches the operating system without losing any unsaved data. It is also known as a restart or soft boot. Unlike a cold boot, which is a complete system startup and reset, a warm boot is only a partial system reset. During a warm boot, some files are preserved, including open windows, custom desktop settings, previously-loaded drivers, and content in RAM.
A warm boot is considered less harmful than a cold boot, as it may cause less disruption to a Windows program or the system as a whole. System administrators may make use of warm booting in order to fix certain issues. It can be used to isolate a problem that may be caused by a system resource that had not been reset or restored during the previous restart cycle.
The warm boot process typically involves pressing the power button on the computer or pressing the Ctrl, Alt, and Delete keys simultaneously. Depending on the operating system, a warm boot may also be triggered by entering a command into a command prompt, such as “reboot”.
Although warm booting may be a useful process, there are potential drawbacks. For instance, hardware drivers and system software may not resynchronize properly, leading to potential software or hardware incompatibilities. Also, certain applications may not properly reinitialize, leading to an unstable system or application crashes.
Overall, warm booting can be a useful tool for administrators to troubleshoot their systems, but should only be used after exhausting other options.