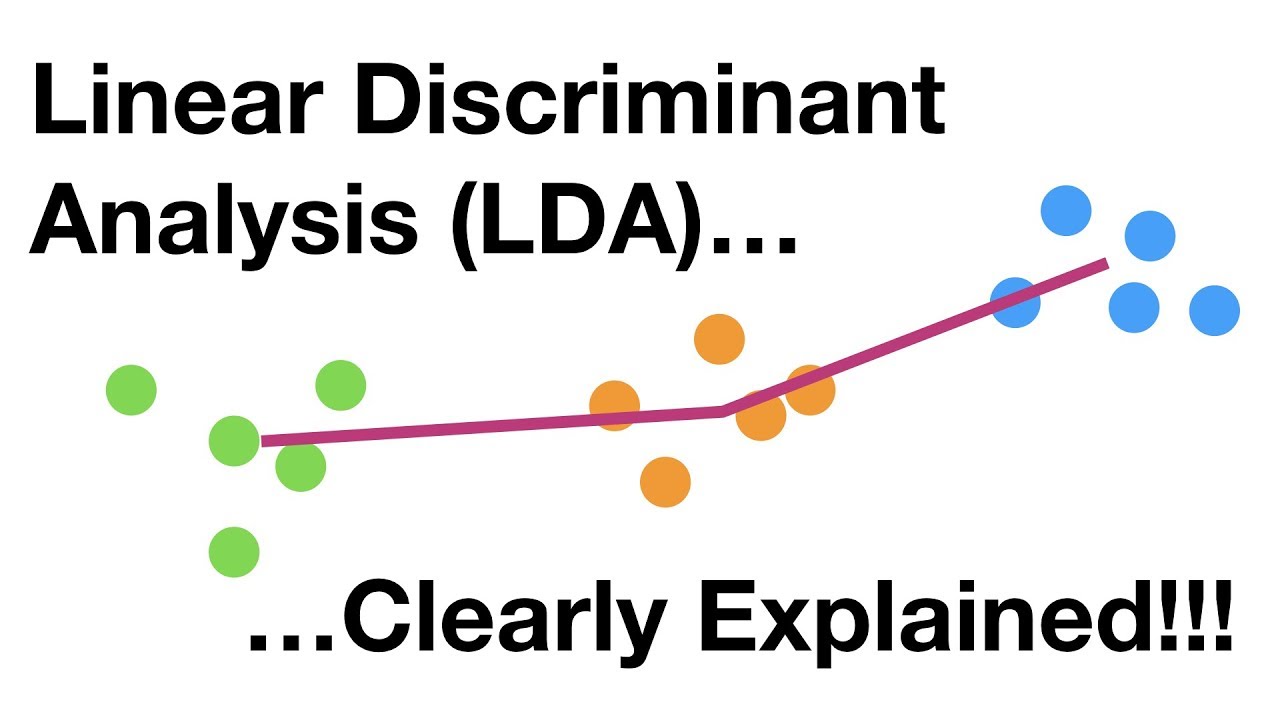
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) is a statistical method used to classify a set of data points into predefined groups. It is used in many different fields such as computer vision, image processing, pattern recognition, genetics, finance, managerial science, social science, artificial intelligence, and bioinformatics. This method was developed in 1936 by Ronald Fisher and is a supervised learning algorithm. It works by finding the maximum separation between different classes of data and can be used to distinguish between two or more classes.
The linear discriminant analysis is based on the assumption that the data comes from a normal (Gaussian) distribution and consists of multiple features or characteristics of data which can be used to classify them into different categories. The method creates a linear combination of input variables (features) and uses a linear separating surface for prediction. This linear combination can be used to measure how well it can classify a particular data point into one of the predefined classes.
This method is used in many different applications. It is used in facial recognition systems to distinguish among different people, medical diagnosis to classify diseases, credit card fraud detection, and object detection in computer vision. It is also used for marketing applications, such as customer segmentation and market basket analysis.
Linear discriminant analysis is relatively simple to understand and implement. It is computationally efficient and flexible for use in different types of data. The method requires knowledge of linear algebra and probability distributions to understand its implementation.