Making sure your online activity is secure should be a top priority. But, which service will deliver the best results?
VPNs and proxy servers are two popular options that can shield users from prying eyes – but do they offer similar levels of protection? A closer look reveals some distinct differences between these technologies: while one helps preserve user privacy, the other may not provide complete anonymity.
The debate about what is best has been going on for a long time on the Internet, both in blogs and on social networks.
Proxy vs. VPN: Which One is the Best?
Let the debate begin! Proxy servers vs. VPN apps: Who’ll win? Both are handy encryption and IP-hiding technologies that provide the ability to obscure a user’s online identity with the intention of accessing blocked or restricted content. pic.twitter.com/F9h9GrWP4d— IPBurger (@IPBurger) March 3, 2019
So we decided that we would just as honestly and impartially tell you everything you need to know to make your choice.
Table of Contents
- What Is a Proxy Server and How Does It Work?
- What Is a Virtual Private Network and How Does It Work?
- The Main Similarities of Proxy and VPN
- The Main Differences Between VPN and Proxy
- Can Proxy and VPN Work Together?
- Proxy vs VPN: Which One Should You Choose?
- Conclusion
What Is a Proxy Server and How Does It Work?
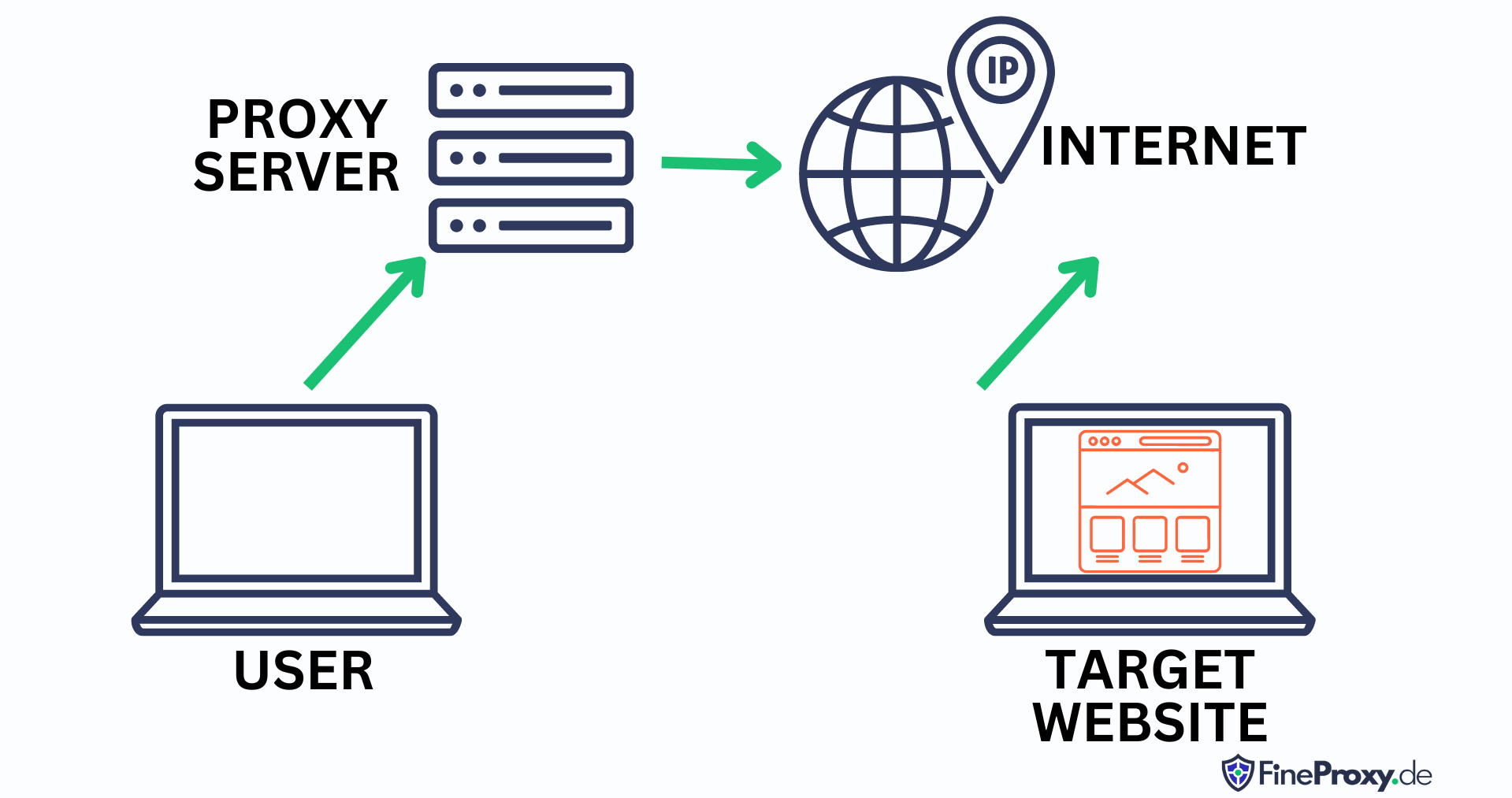
Proxy servers are powerful tools that can be used to unlock a world of previously inaccessible possibilities. By hiding users’ device IP addresses, they not only protect certain types of web activity, but also provide access to geo-restricted websites.
The following types of proxy servers are most commonly used:
- SOCKS5 is great for file sharing and video streaming;
- HTTP works well in countries with high levels of internet censorship – perfect for those who require greater privacy online;
- Transparent proxies come into play when restricting specific sites; such as the case might be at public libraries, wanting their patrons unable to view Facebook pages.
There are also forward, anonymous, high anonymity, distorting, data center, residential, public, shared, and SSL proxies.
How Does It Work?
HTTP proxies are widely used as a means of accessing geo-restricted websites and pages. Through internet access, these proxy servers forward data to your browser for viewing – much like an intermediary between you and the final server. It’s important to note that this method does not provide encryption security; only identity anonymity from the web page itself.
A SOCKS5 proxy can be employed to secure many types of data transfers, such as peer-to-peer file sharing and email. It safely restricts all connection attempts from malicious applications at the 5th layer, while also allowing for use with a wide range of programs that support proxying — making it an ideal choice beyond your standard web browser.
Transparent proxies are an essential part of many online networks, offering users control and monitoring over web traffic. Commonly used in educational institutions, workplaces, or public spaces like cafés to block access to certain websites such as social media or streaming services; they also serve businesses by ensuring employees don’t become distracted from their work tasks whilst using the company’s bandwidth efficiency.
Pros & Cons of Using Proxy Servers
Proxies are a fantastic way to improve and enhance your online experience:
- They provide an extra layer of security for personal data, allowing you to browse the web with total peace of mind knowing that unwanted eyes won’t be able to see what’s happening.
- For parents concerned about their children accessing inappropriate content or websites, proxies offer powerful tools in terms of restriction options which can block access from specified sites entirely.
- On top of this they have excellent caching capabilities which mean certain pages load quicker than ever before — no more waiting around.
Despite its potential to increase digital security and privacy, using a proxy server does come with drawbacks:
- Free proxies may be inadequate when it comes to providing reliable protection.
- Browsing history logs can easily build up on the server – visible only through an IP address, which is often unencrypted; plus requests from your device may not always be 100% encrypted, leaving sensitive data vulnerable to hacking.
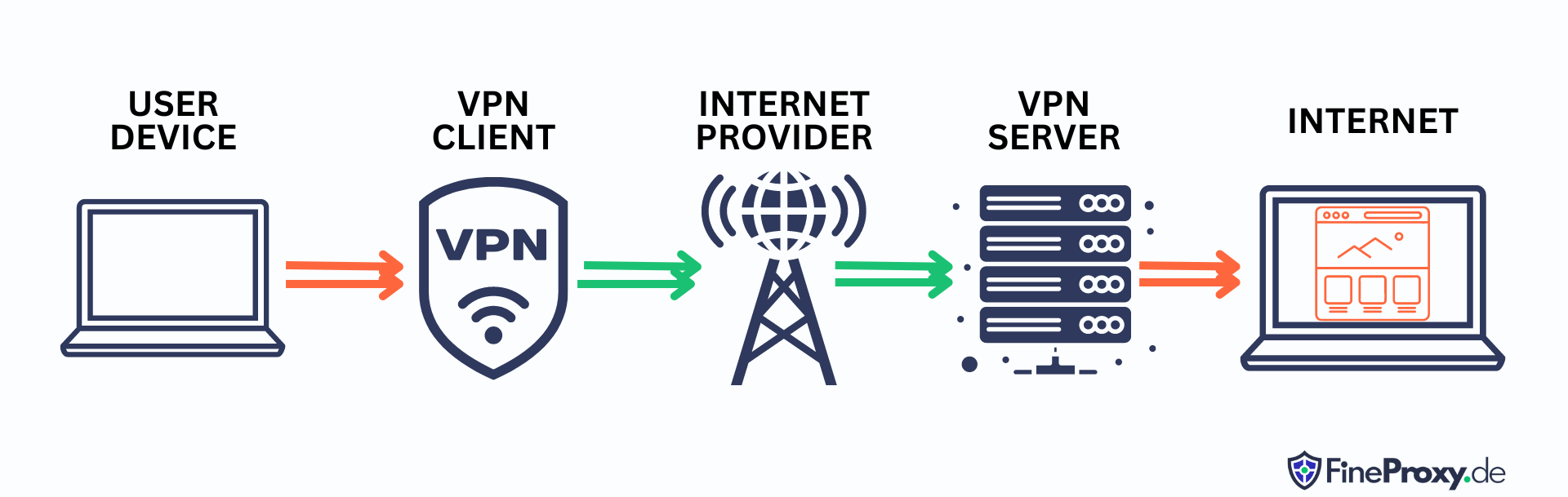
What Is a Virtual Private Network and How Does It Work?
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is a private network that helps secure and protect your browsing habits, even when accessing the internet through less-than-secure networks.
It’s like having an invisible courier – taking website data from the source to your computer while keeping prying eyes away by encrypting information with strong encryption standards as it travels across cyberspace.
On top of this advanced protection, you also benefit from being able to hide where in the world you are really located; enabling access to geo-restricted content like movies or series usually only available on certain regions. Businesses can use VPNs too, offering employees remote access to their company’s resources via protected IP addresses wherever they may be working around the globe.
The VPN types are the following:
- Corporate VPNs enable businesses to securely connect their employees and devices from any remote location, providing a high level of protection for users.
- Individual-focused services offer unparalleled privacy for individuals seeking online security.
How Does It Work?
To keep your data out of the wrong hands, a VPN can be an invaluable tool to encrypt communication between two points – from your device to a website or service overseas.
Plus, it stops potential hackers lurking in the network by intercepting traffic, so they can’t get hold of any sensitive information like passwords and bank details.
And for that extra layer of privacy assurance, it also masks identity-revealing IP addresses away from ISPs and employers who try monitoring web activity!
Finding an agreement that suited both parties, we decided to explore the similarities and differences between VPNs and proxy servers.
Pros & Cons of Using a VPN
A VPN is a powerful tool that can help keep your network and data secure:
- A VPN offers unmatched protection for your network and data, encrypting internet traffic to make sure it can’t be intercepted.
- Plus, those who game online have the added benefit of avoiding IP bans and DDoS attacks with a reliable VPN.
- Bandwidth throttling isn’t an issue either; when encrypted web traffic confuses ISPs they won’t know how much bandwidth you’re using so speeds aren’t compromised during peak hours.
A VPN might seem like the right choice, but there are potential drawbacks:
- Not only could your internet connection be slowed due to its routing through multiple servers, but free services may not keep you safe — they can collect and sell data without infrastructure or updated security measures in place.
- An added monthly cost of a subscription could make this service less viable for some users.
4 Main Similarities of Proxy and VPN
Finding commonalities between VPNs and Proxy Servers, we recognized four primary ways in which the two technologies align:
- Proxies and VPNs offer customers the chance to explore a whole new world of previously blocked online services – all anonymously. By changing their IP address, users can access content that may have been out of reach before.
- With VPNs and proxies, third-party routers are used for enhanced security. While you have the option of setting up an internal server for either service, it’s typically better to source them from a trusted external partner.
- Both are powerful tools that make it easy to decide who has access to what. By using proxies, employers can keep their employees focused on the task at hand by blocking off certain websites.
- If privacy is your priority, neither proxies nor VPNs alone can offer complete protection. While a VPN may be more effective at masking network traffic and hiding one’s location, it still has potential technical flaws that could lead to data collection by commercial parties or governments.
7 Main Differences Between VPN and Proxy
Let’s dive into the nuances between virtual private networks (VPNs) and proxy servers, two solutions that offer a range of features for navigating digital environments.
| Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|
| Proxy servers provide coverage for only one specific site or application at a time. | With a VPN, users can securely access the web with complete peace of mind – every website and app visit is encrypted. |
| When utilizing proxies in conjunction with the Internet, client anonymity can be achieved by employing an anonymous network ID instead of revealing the real IP address. | By using a virtual private network (VPN), users’ IP addresses are not concealed. |
| Proxies deploy FTP (File transfer protocol), SMTP (Simple mail transfer protocol) and HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol). | Virtual Private Networks rely on PTTP (Point-to-point Tunneling Protocol) or L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol). |
| Proxy hides the original IP address of a user while browsing, it does not offer encryption protection. | With VPN, all your outgoing traffic is securely encrypted and kept private. |
| Proxy servers do not provide the virtual access to remote networks. | A Virtual Private Network (VPN) provides the security and convenience of a private network without sacrificing accessibility.> |
| It offers service directly in your browser. | It works by creating an encrypted link between its host server and the firewall for extra protection. |
| With Proxy, your data is vulnerable to infiltration. | VPN provides an extra layer of protection for valuable information with its high level security capabilities. |
When it comes to technology, the terms “VPN” and “VPN proxy” can be used interchangeably. In other words, a VPN server is essentially an HTTPS (TLS/SSL) server – making them remarkably similar to virtual private networks.
Security and Privacy Differences Between Proxies and VPNs
Protect your privacy and security online with either a proxy or VPN. With proxies, you can gain access to restricted websites by bypassing geographical restrictions — but bear in mind that they don’t offer encryption of user traffic against snoopers. For the highest level of anonymity possible, opt for a VPN instead: this encrypts all internet activities so even if someone tries to track what you’re doing online it will be blocked from view!
Speed and Performance Differences Between Proxies and VPNs
Proxies and VPNs are commonly used to protect user data when connected to the Internet, but they each offer distinct advantages in speed. While a proxy’s implementation is simpler so it can provide faster connections at times due to its lack of encryption, VPNs tend have variable speeds which depend on several factors like server location, total users accessing the network or even different security protocols that may be implemented.
Can Proxy and VPN Work Together?
If you’re considering combining VPNs and proxy servers, it is possible – but most likely not worth the effort.
By combining the power of a VPN and proxy, you can protect yourself from prying eyes while surfing online. Your connection will be securely routed through multiple anonymous servers so that your real IP address stays hidden — twice over. This extra layer of encryption offers superior protection against tracking measures ensuring absolute privacy even if one or both connections have vulnerabilities.
While configuring both can be a complex task, having two middlemen won’t necessarily bring much benefit to your internet connection speed or security. We recommend selecting one service over the other for optimal results.
Do I Need a VPN and a Proxy at the Same Time?
VPNs and proxies both provide much-needed privacy when navigating the internet, but do you NEED to use them together? Not typically!
While it’s possible to take extra measures by rerouting through a proxy server for added anonymity, in most cases one or the other will suffice. So there’s no need to worry about using two different methods – just pick one that provides maximum security and enjoy surfing without worrying about compromising personal information.
Proxy vs VPN: Which One Should You Choose?
Whether you’re looking to secure your privacy or just obscure an IP address, proxy servers and VPNs are both valuable solutions.
| Feature | Proxy | VPN |
|---|---|---|
| Can be used to bypass geo-restrictions | Yes | Yes |
| Number of users | 1 | Unlimited |
| Slows down browsing speeds | Yes | Yes |
| Encrypt IP address | Yes | No |
| Encrypt web activity | No | Yes |
| Coverage | 1 website or app | All website or apps |
| Compatible with streaming and gaming | Yes | Yes |
Let us now tell you a little more about the advantages and use cases of these two types of digital protection.
When Should You Use a Proxy?
Businesses are often limited in their ability to leverage web data for marketing and sales purposes due to barriers like geo-blocking or IP blockers. To help bypass these issues, proxy servers can be set up to mask an individual’s actual location by hiding their IP address from the internet geolocation techniques used online.
Alternatives such as free VPN services exist but may not always provide secure protection; Amazon Prime is a great example of this, since some users are blocked based on where they’re located! Paid VPNs remain one of the best options when it comes to maintaining privacy while accessing global websites.
Although VPNs offer greater privacy and security, the additional layers of encryption can lead to slower connection speeds than that which is found with proxy servers. When using a virtual private network for data protection, many users must sacrifice speed in order to experience increased levels of safety online.
Summing up:
- To gain access to geo-restricted content;
- Not slow down Internet connection.
When Should You Use a VPN?
VPNs offer enhanced security compared to proxy servers. By encrypting all the user’s network traffic, they provide a stronger layer of protection for online activities and guard against ISP tracking or cyber criminals trying to steal personal data. Furthermore, both proxies and VPNs conceal users’ IP addresses from third parties — but with an added bonus: VPN also blocks any sensitive information that leaves your device! So if you’re serious about protecting yourself while browsing the internet, it may be worthwhile opting for a secure virtual private connection over standard proxies.
When it comes to remote work, VPNs offer the best protection for any device you might use – from computers and mobile phones to televisions and modems. Not only do they secure your overall system, but also let you access office machines or systems no matter where in the world you are located.
The downside is that due to distance between your own device and a dedicated VPN server, processing times can be slow – imagine sending instructions halfway around the globe before getting an answer. Proxies on the other hand cover specific applications or devices only, making them not suitable when it comes to protecting all of your tech at once.
Summing up:
- Protect sensitive data;
- Work on a system level.
Are you still confused about the differences between VPNs and proxies? We recommend you watching the video by ThioJoe. In this video, he explains the differences between proxies and VPNs, and when you might want to use each.
Conclusion
When it comes to accessing geo-restricted content, there are two ways of doing so – proxies and VPNs. While free or low-quality proxies may be tempting for users on a budget, VPN is the best route when security is paramount as they provide much higher levels than their lesser counterparts.
For personal tasks where safety isn’t an issue, proxy servers allow access to blocked websites at no cost while still providing IP masking services; however businesses must take greater care in selecting secure solutions such as those offered by reputable VPN providers that offer larger networks with enhanced ease of use capabilities.





