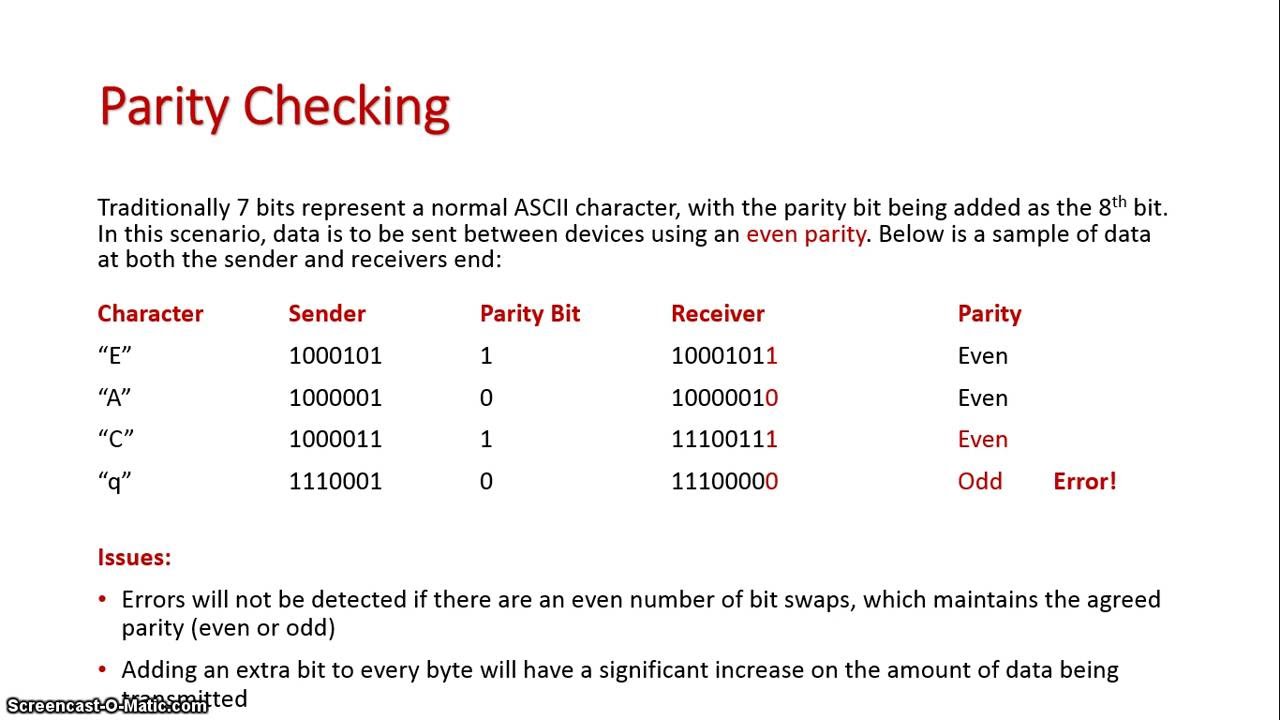
Parity check is a simple, common technique used in computing to ensure data integrity. It works by redundantly storing information about the data in the form of a parity bit. A parity bit is a single bit stored alongside a group of bits such as a byte, word, or block of data. The parity bit is used to detect errors in the data upon transmission, as a single bit change will cause the parity bit to disagree.
The type of parity used is determined by the parity scheme chosen. There are two types of parity schemes: even and odd parity. In an even parity scheme, the parity bit is set to one if the number of bits in a given set with the value one is odd; otherwise it is set to zero. In an odd parity scheme, the opposite is true: the parity bit is set to one if the number of bits in a given set with the value one is even; otherwise it is set to zero.
When transmission errors occur, the creator of the data can detect mismatches between the parity bit and the data, thereby alerting them to check for data integrity. While parity bit checks are largely superseded by more sophisticated checking mechanisms, such as Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and cryptographic hashes, they are still commonly used as they are simple to implement.
Parity check is a useful mechanism that can be used to detect errors in data, although it has its limitations. In particular, parity check can only detect single bit errors, and therefore cannot be used to discover multiple bit errors or errors that don’t directly affect the parity bit itself.