Relational Database, sometimes referred to as “RD”, is a type of database management system (DBMS) which organizes data into related tables. This type of DBMS utilizes a Structured Query Language (SQL) to facilitate interaction with the data stored within the database and encourages data integrity. It was first introduced by IBM researcher E.F. Codd in 1970, and has since become the most widely used form of database management worldwide.
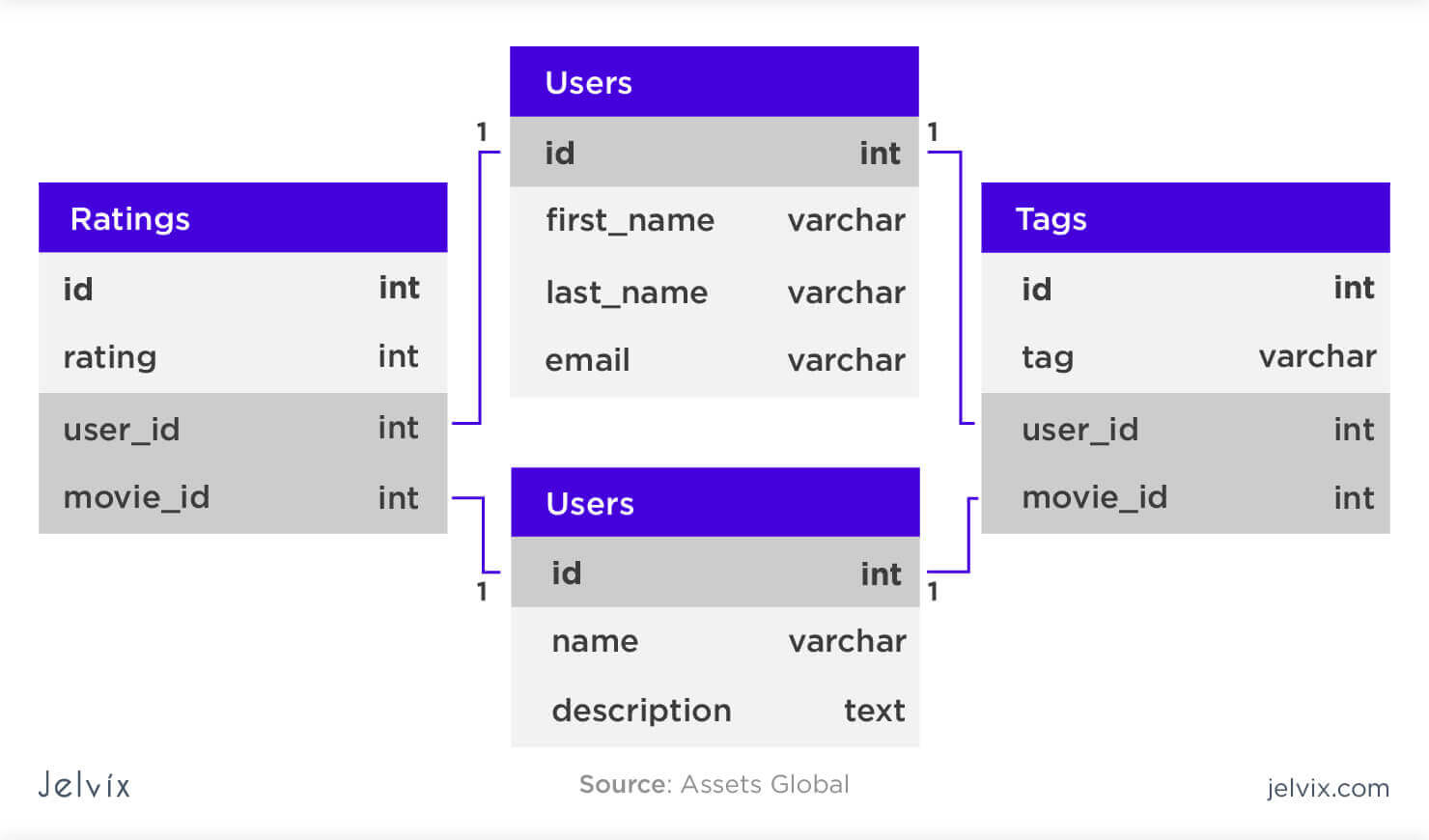
Relational database systems are comprised of several components, including tables, records, views, relationships, and triggers. Each component has a specific purpose and utilizes the relational model to join tables together and access the various data. Tables are the fundamental component of a relational database, and are comprised of rows and columns. Each row is known as a record, and each consists of fields which describe data points associated with that particular record. Views are similar to tables, in that they contain data, however the data represented cannot be altered. Additionally, relationships are essential components of a relational database which allow a user to establish links between different tables. Triggers are events that are automatically enacted when the database is accessed.
Relational databases have numerous advantages, such as easy manipulation of data, a secure storage structure, and little need for maintenance. Queries are also possible to summarize, compare, group, and sort data for special reports, and combined with efficient indexing, make it ideal for data that must be updated frequently. Furthermore, relational databases are able to handle large amounts of data, as well as the huge concurrent user access which is necessary for many websites.
In spite of their numerous advantages, there are some disadvantages to using relational databases. These include the high cost of the hardware and software needed to operate them, the relatively slow query speed, and potential data redundancies. Additionally, the data must always be stored in a tabular format in order to work within a relational database.
Despite their limitations, relational databases remain the gold standard in database management and have been the backbone of websites, online stores, and data tracking for the past decades. With continual improvements being made to relational databases, and the usage of increasingly powerful computer hardware, they will remain the standard for years to come.