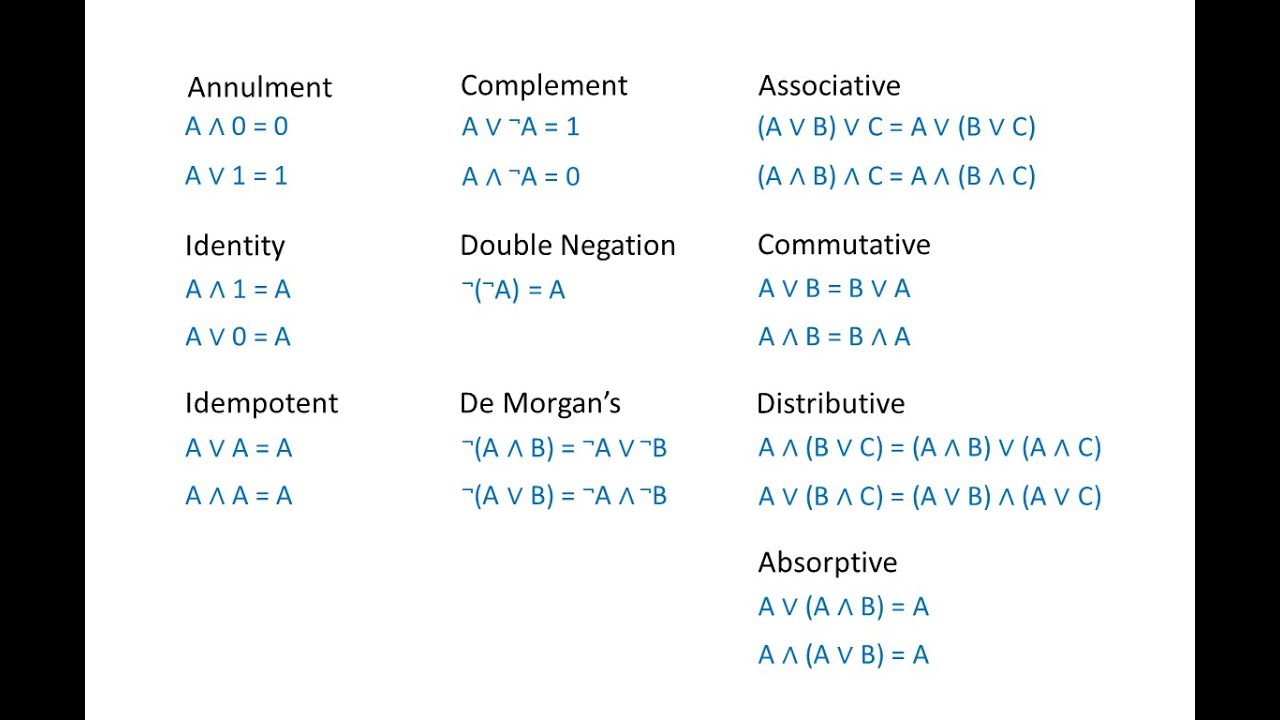
Boolean algebra, named after 19th century mathematician George Boole, is a logical calculus system used to represent and reason about the truth values of variables. It is an important tool for digital logicians, computer scientists and engineers working with computer engineering and electronics.
Boolean algebra is based on two distinct values, the “true” and the “false”. This particular logic system is based on the idea that any statement can be described in a way that either true or false with either a “yes” or “no” answer. The algebra is made up of operations such a join (or, +), elimination (not, -), intersection (and, &), and union (or, |).
In Boolean algebra, variables are associated with the different sets of binary values, with a value of either 0 or 1. Boolean operations such as combining multiple variables together via addition and multiplication, as well as comparisons such as more than, less than, and equal to, can be used to represent the logic between variables.
Boolean algebra and its logic gates are fundamental to the base work of computing, since it aids in managing binary coding systems. With it, large and complex logical statements can be managed by breaking them down into smaller, binary chunks. This in turn enables more efficient storage and allows for easier and faster parsing of data by computers. The fundamentals of Boolean algebra can be seen in almost any electronic device, from the inner workings of a computer or television, to the cellular telephone or pocket calculator. Boolean algebra is seen as a successful tool for digital logic and has been used to create many useful devices in electronics.