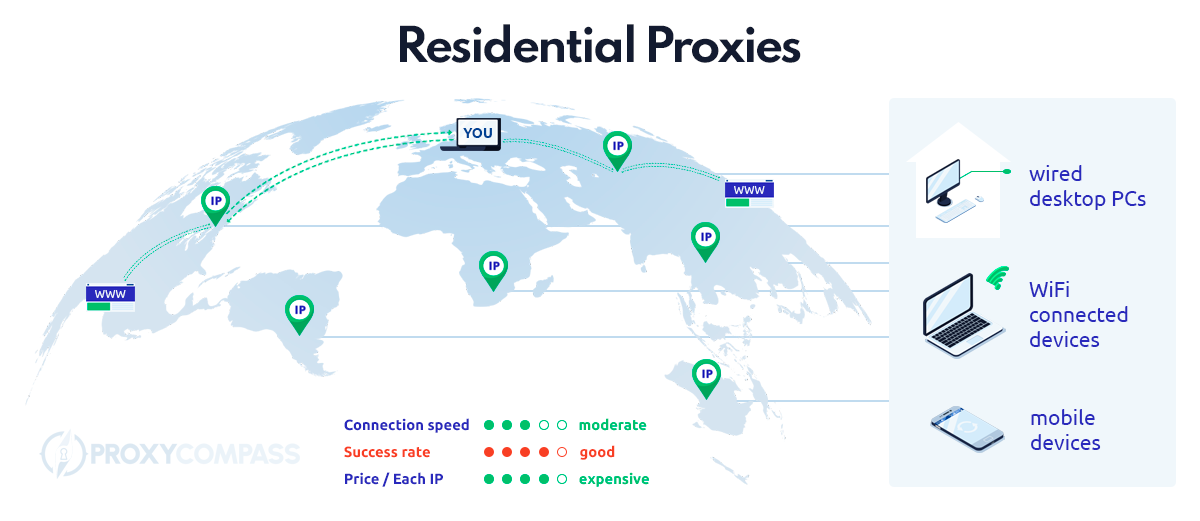
With residential proxies, a mobile or desktop device of a private Internet user is used as a proxy. This often happens without the user’s knowledge; a user has proxy software installed on their gadget and someone uses their gadget and IP address as a proxy server.
Where do such proxies come from?
A proxy provider buys so-called “installations” from software developers (free games, add-ons, etc.). In other words, the proxy provider negotiates with programmers of free applications and offers to monetize their applications by integrating the code of the proxy server, i.e. the proxy software, into their source code.
A user who has downloaded a corresponding application agrees during installation that resources of his device may be used by third parties. As soon as he accesses the Internet, the IP of his device is added to the pool of the proxy provider and is available to customers of the proxy service as a proxy.
Are residential proxies legal?
Yes, at least large proxy providers operate legally (though only after a series of scandals). This means that today, if a user downloads a free program or installs an add-on in his browser, he agrees to the TOS (Terms of Service) conditions – although these are usually not actually read.
What are the options for users of a residential proxy service?
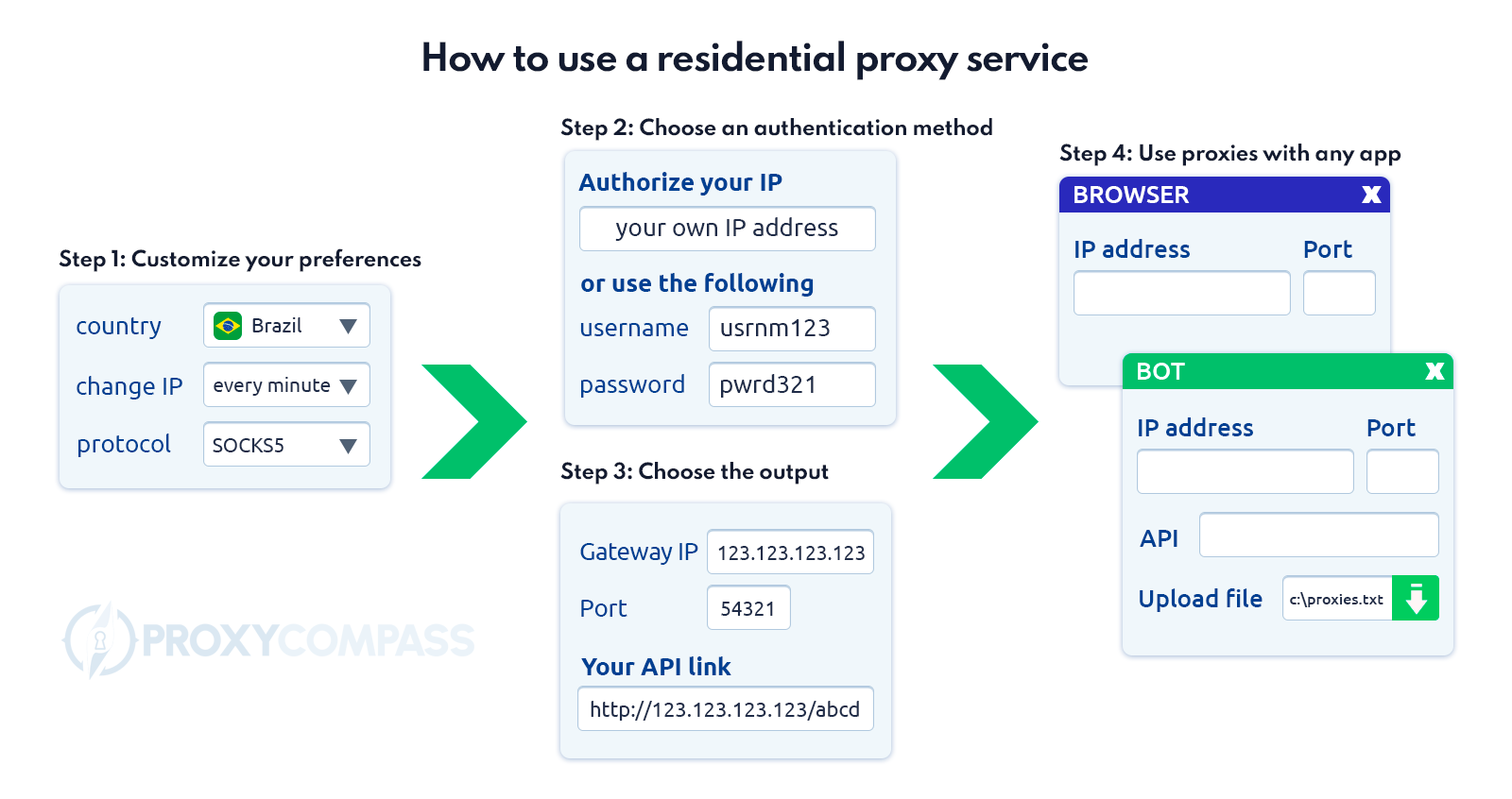
The user area allows the user of a residential proxy service to customize the following parameters:
- Create a separate profile for a specific country, state, city
- Select ideally suited internet providers
- Select the IP type he wants to have at the output (mobile or desktop)
- Select the IP change frequency. For example, to have the IP change each time the page is reloaded, or to save an IP as long as possible (so-called sticky IP), but in reality, it does not take more than a few minutes.
After completing the profile settings, the customer receives a so-called gateway IP address with a non-standard port that looks something like this:
123.123.123.123:54321
In this case, 123.123.123.123 – is the IP address of the proxy service, which is the same for all its clients, and 54321 is the port where the client gets the output IP addresses corresponding to the settings of the created profile.
How to use such a gateway IP?
All one needs to do is to enter the gateway IP into the network settings of their browser or bot, and the connection will run through the devices defined in your profile – e.g. only a mobile connection and only residents of North Rhine-Westphalia who solely use Vodafone service provider – with a certain frequency of change (e.g. every time the client of the proxy service reloads the page of their browser, they will receive an IP address of a new device that corresponds to the settings of the created profile).
Advantages of residential Proxies
- Low probability of blocking on a target page
- The IP pool of the large residential proxy providers contains a huge number of proxies (10+ million) – there are always suitable proxies to choose from
- Flexible API (application programming interface) settings; the ability to create multiple profiles for different geo-sites, etc
- Accurate geo-targeting (up to a specific city)
- Choice between desktop and mobile device
- Selection of a specific internet provider (Vodafone, T-Mobile, etc.)
Disadvantages of residential proxies
- Unstable speed, connection breaks
- Impossible to keep a certain IP for more than 30 minutes (max.)
- Customer of the proxy service must pay the traffic volume separately
When are residential proxies used?
Residential proxies are always useful when working with websites that have strong antibot protection and geo-dependent output: postings in Craigslist, parsing of regional Google editions (SERPs), analysis of product placement on amazon.com, booking.com, etc.