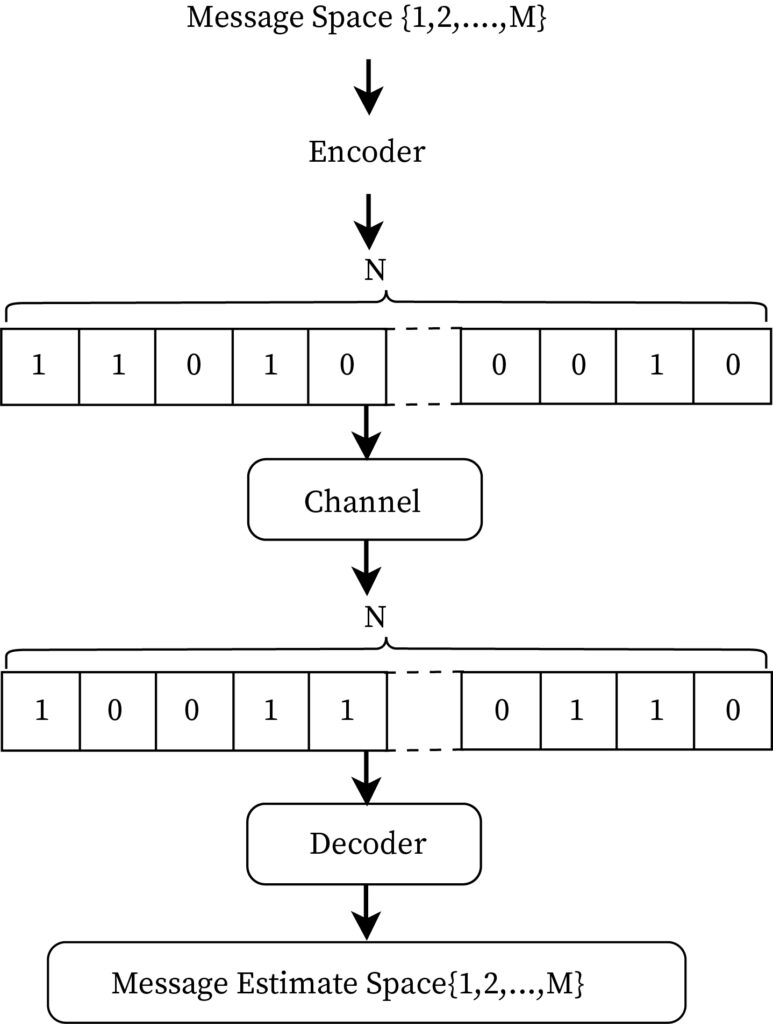
Coding Theory is a branch of mathematics and computer science that studies the properties of communication systems in which data is encoded for transmission over a noisy channel, and the algorithms for the recovery of the original data. It was developed in the 1940’s and 1950’s by Claude Shannon in his groundbreaking work on the mathematical theory of communication.
The main goal of coding theory is to design and analyze mathematical methods for transmitting information over a communication channel with the least possible amount of error; these methods are referred to as error-correcting codes.
Error-correcting codes involve the addition of redundant data, known as parity bits or checksums, to the original data. This redundancy allows the receiver to detect errors by checking the accuracy of the received data against the checksum. If errors are found, the receiver can then use various algorithms to reconstruct the original data.
Another area of coding theory is cryptography, which involves the use of codes and ciphers to encrypt a message so that it can only be decrypted by the intended recipient. Cryptography has wide use in the field of computer security.
Coding theory has applications in a wide range of areas, including digital communications, storage of digital information, satellite communication systems, and digital cash systems. It is an important part of digital signal processing, where it is used to design efficient and reliable communication systems.