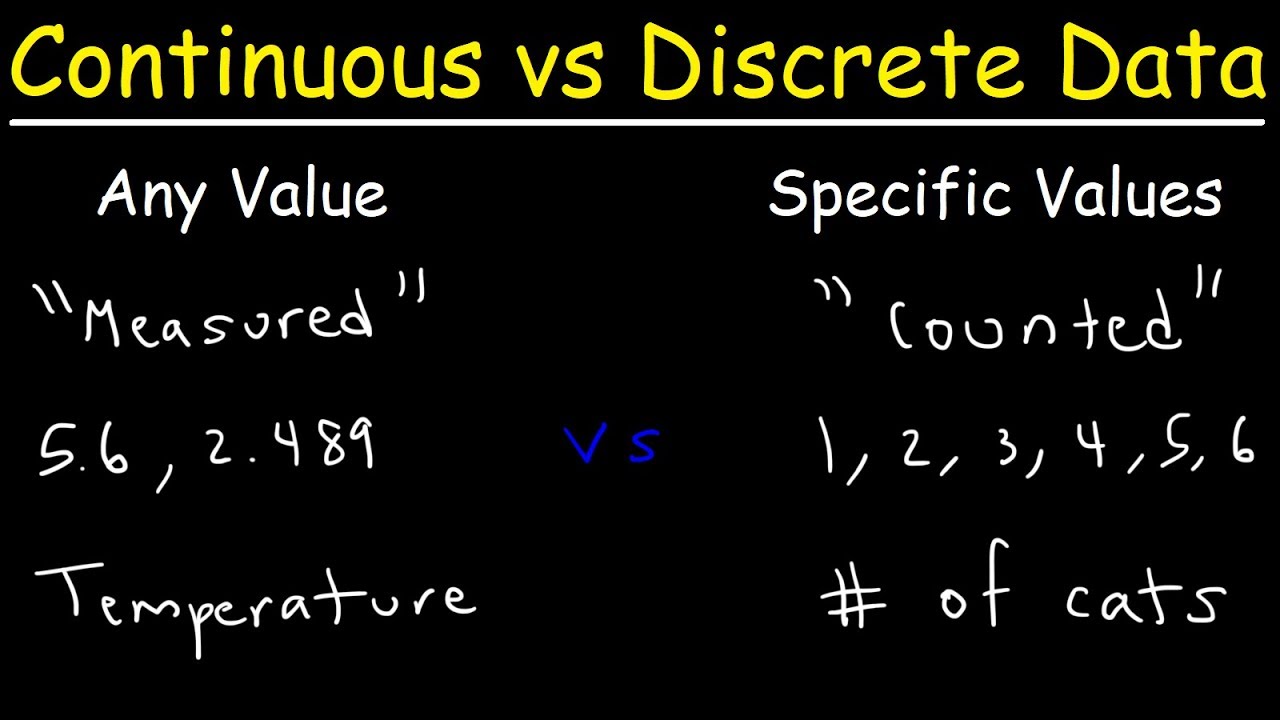
Discrete data is a type of data that occurs in whole numbers and is used to measure categorical variables. It is often referred to as “count data.” In contrast to continuous data, discrete data can only assume a limited number of values within a given range.
In computer science, discrete data is often used to describe situations with multiple outcomes that are all distinct and separate. For example, a database could contain discrete data that tracks information such as a customer’s age, gender, or zip code. Other examples of discrete data include counts of customers who have visited a website, the number of emails sent, or the number of sales in a given time period.
Discrete data is typically stored in a database or numerical array and can be analyzed using various statistical methods. It can be used to create a histogram to visualize the data, to calculate the mean and standard deviation of the data, or to predict future results based on past results.
Discrete data has many applications in the fields of computer science, mathematics, and statistics. For example, it can be used to model customer behavior, analyze financial data, and create risk models. In addition, it can be used to calculate probabilities and make predictions in engineering and medical fields.
Discrete data is an important concept for computer scientists, mathematicians, and statisticians. It can help to reveal patterns in real world data and can provide insights into how to act on those patterns. With proper analysis, discrete data can be used to help organizations make more effective decisions and help create a better understanding of the world.